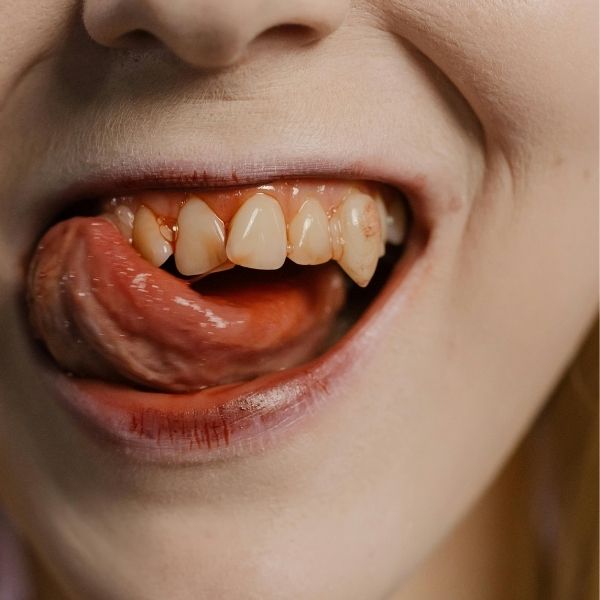
Bleeding gums are a common dental issue that many people experience at some point in their lives. While they may seem like a minor problem, bleeding gums can be a sign of underlying oral health issues that, if left untreated, could lead to more severe complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for bleeding gums is crucial for maintaining both oral and overall health. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about bleeding gums, including why they occur and how to prevent them.
Causes of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can be caused by several factors, ranging from temporary irritation to serious dental conditions. Here are the most common causes:
- Gingivitis: One of the leading causes of bleeding gums is gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Gingivitis occurs when plaque builds up on the teeth and along the gumline, leading to inflammation. This buildup irritates the gums, making them swollen, red, and more likely to bleed during brushing or flossing. If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
- Periodontitis: When gingivitis is left untreated, it can develop into periodontitis, a more advanced and severe form of gum disease. Periodontitis affects the tissues and bones that support the teeth, leading to gum recession, loose teeth, and, in extreme cases, tooth loss. Bleeding gums are a common symptom of periodontitis, and if you notice persistent bleeding, it’s essential to seek dental treatment immediately.
- Improper Oral Hygiene: Incorrect brushing and flossing techniques can also cause bleeding gums. Using a toothbrush with hard bristles or brushing too aggressively can damage your gums and lead to bleeding. Similarly, flossing too forcefully or incorrectly can cause irritation and bleeding between the teeth.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain vitamins, particularly vitamin C and vitamin K, can lead to bleeding gums. Vitamin C is essential for maintaining healthy gum tissue, and a deficiency can cause gums to become weak and prone to bleeding. Vitamin K helps with blood clotting, and a lack of this vitamin can make it more difficult for your body to stop gum bleeding.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially in women, can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to bleeding. Pregnant women, in particular, often experience “pregnancy gingivitis,” which causes their gums to become inflamed and bleed more easily due to increased blood flow to the gum tissue.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can increase the likelihood of bleeding gums. Blood thinners reduce the blood’s ability to clot, making it easier for your gums to bleed. If you’re taking any medications and notice your gums are bleeding more than usual, it’s worth discussing this with your doctor or dentist.
- Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease and bleeding gums. The toxins in tobacco weaken the immune system, making it harder for your body to fight infections like gingivitis and periodontitis. Smokers are more likely to experience gum bleeding due to their increased risk of gum disease.
Symptoms Accompanying Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can often be accompanied by other symptoms that may indicate a more severe problem. If you notice any of the following alongside bleeding gums, it’s important to consult your dentist:
- Swollen, red, or tender gums: Inflamed gums are a key sign of gum disease and should not be ignored.
- Receding gums: When gums start to pull away from the teeth, it can expose the roots, making your teeth more vulnerable to decay and sensitivity.
- Persistent bad breath: Gum disease can cause chronic bad breath due to the buildup of bacteria.
- Loose teeth: If your teeth feel loose or if they shift, it could be a sign of advanced periodontitis.
- Pain when chewing: Discomfort when chewing can also signal an issue with your gums or teeth.
Treatment for Bleeding Gums
The treatment for bleeding gums will depend on the underlying cause, but there are several general measures you can take to improve your gum health:
- Improve Your Oral Hygiene Routine: One of the most effective ways to treat bleeding gums is to maintain a consistent and proper oral hygiene routine. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, and be sure to floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between your teeth. Using an antiseptic mouthwash can also help reduce bacteria and plaque buildup.
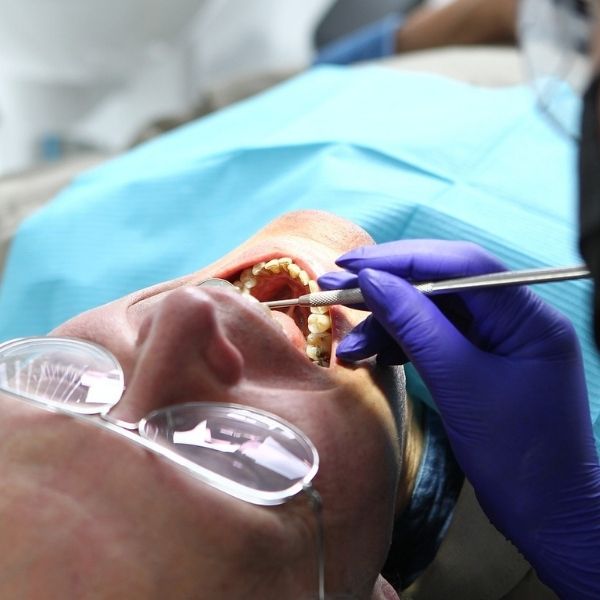
- Schedule a Dental Check-Up: If your gums continue to bleed despite maintaining good oral hygiene, it’s time to see your dentist. During a check-up, your dentist will examine your gums and teeth, remove any plaque or tartar buildup, and recommend treatment if necessary. If you have gingivitis or periodontitis, professional cleaning, scaling, and root planing may be needed to remove plaque from beneath the gumline.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for gum health. Make sure you’re getting enough vitamin C, which can be found in fruits like oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers, as well as vitamin K, found in leafy greens such as spinach and kale.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria in your mouth, reducing the risk of plaque buildup and gum irritation.
- Use a Saltwater Rinse: A saltwater rinse can soothe irritated gums and reduce inflammation. Mix a teaspoon of salt into a glass of warm water, swish it around in your mouth for 30 seconds, and spit it out. This can be done once or twice a day to help treat bleeding gums.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your gum health. Smoking weakens your immune system and makes it harder for your gums to heal from infections, making gum disease and bleeding gums more likely.
Preventing Bleeding Gums
Prevention is the key to avoiding bleeding gums and gum disease. Here are some tips to keep your gums healthy and reduce your risk of bleeding:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, using gentle circular motions to avoid irritating your gums.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food debris from between your teeth.
- Use an antiseptic or antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria that can cause gum disease.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support your gum health.
- Avoid tobacco products, as they significantly increase your risk of gum disease.
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups.
When to See a Dentist
If you experience persistent or excessive bleeding gums, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Bleeding gums can be an early warning sign of gum disease, and catching it early can prevent it from progressing to more severe stages. Additionally, if your bleeding gums are accompanied by other symptoms such as gum recession, loose teeth, or persistent bad breath, you should seek professional advice.
Your dentist will be able to diagnose the cause of your bleeding gums and recommend a treatment plan to restore your gum health. Early treatment is essential to prevent the loss of teeth and other complications associated with advanced gum disease.
Bleeding gums may seem like a minor issue, but they can be a sign of serious dental problems such as gum disease. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for bleeding gums, you can take proactive steps to maintain healthy gums and prevent more severe oral health issues. Remember, good oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular dental visits are your best defenses against bleeding gums and gum disease. If your gums are bleeding frequently, don’t hesitate to seek advice from your dentist to ensure your gums stay healthy and strong.